
In some operating systems, all parts or certain parts of the process can be combined or repeated at different levels. The third part of the process, often referred to as “advanced formatting”, usually refer to as the process of generating a new file system. Partitioning is a generic term in the second part of the process that makes data storage device visible to the operating system. The first part of the formatting process that performs basic media preparation often considered as “low-level formatting”. In some cases, formatting can also create one or more new file systems. Formatting can be divided into three parts.

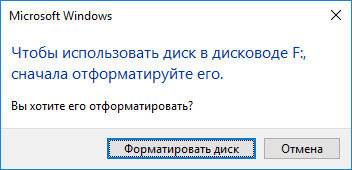
Disk formatting is the process of preparing a data storage device such as a hard drive, sloid state drive for initial use. What is formatting? Formatting a hard drive means to delete all the data on the drive and set a file system to prepare an available space for the operating system. What Does Formatting a Hard Drive Do FAQ.To know the details, please read the article with attention.
#Disk formatting explained how to#
Brief introductions to disk formatting, the purpose of formatting a hard drive, as well as how to format are talked in this post of MiniTool. Programs such as Internet Explorer and databases should be partitioned separately to reduce potential storage media fragmentation.What does formatting a hard drive do? Have you ever asked yourself? The first idea occurs to you might be data loss, but that’s not all. Techniques to reduce defragmentation include partitioning and optimization, which allow users to create logical OS hard drives.
#Disk formatting explained windows#
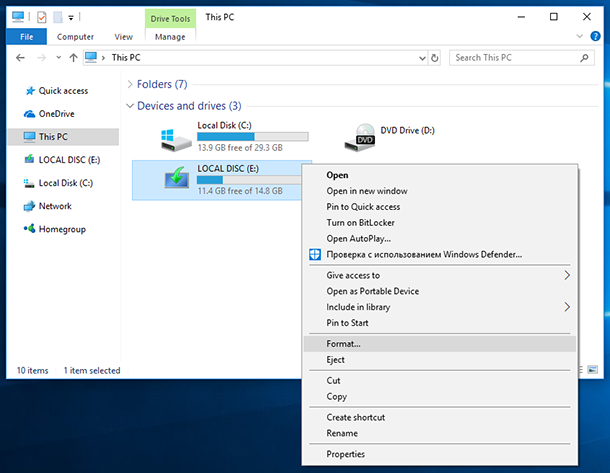
Third-party versions also are available.īack-end processes such as reading and writing storage media are always invisible to users, who are unable to continuously defragment storage devices because of the impact this has on a system's rhythmĭefragmentation tools were introduced to eliminate this issue and are preinstalled in different versions of the Windows OS. Microsoft Windows provides a proprietary defragmenting tool within its OS. Windows-based computers require periodic defragmentation Unix and Linux-based computers do not because of a different design for storing data, even if the same hardware is used. Gradually, both the file and the hard drive become fragmented, and the computer becomes very slow as it needs to search in various places to open a file. Supplementary modifications are stored to even more locations. The saved modifications for a file are usually stored at a hard drive location that is different from that of the original file. Fragmentation occurs gradually as users change, save, or delete files.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
